The Brilliance of Neurosurgeons
April 13, 2024
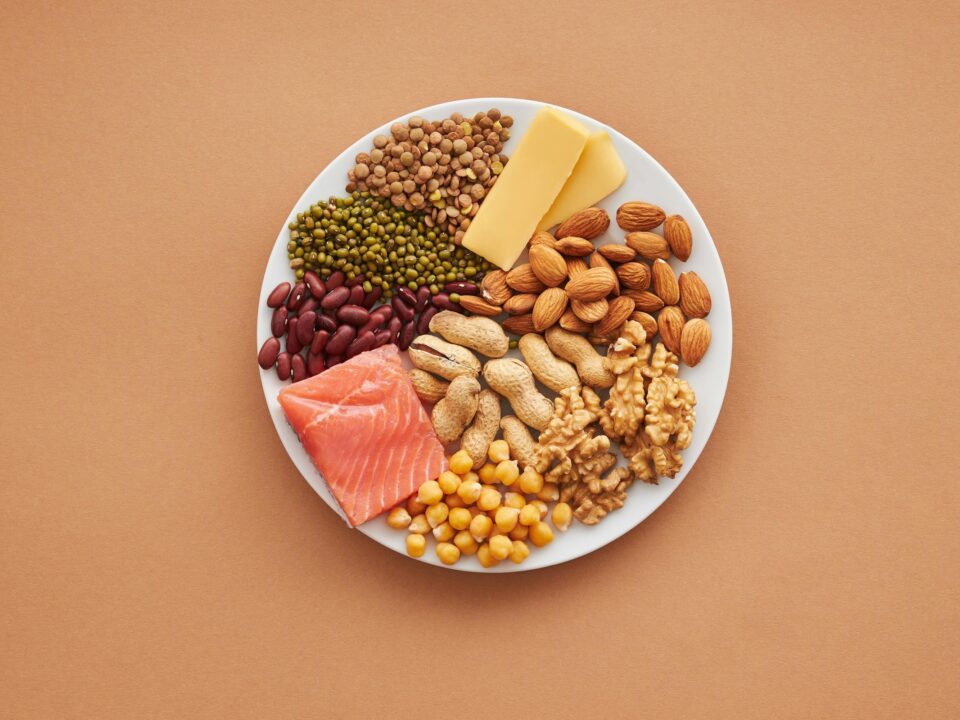
Brain Food: How Early Nutrition Shapes Your Child’s IQ
May 3, 2024Understanding Intelligence: Beyond IQ
Intelligence is a multifaceted concept that encompasses a wide range of cognitive abilities, from problem-solving and reasoning to creativity and emotional understanding. It is not limited to the traditional notion of IQ, which measures specific skills such as logical reasoning and mathematical ability. Instead, intelligence is better understood as a complex interplay of various mental processes and traits.
Types of Intelligence
The theory of multiple intelligences, proposed by Howard Gardner, expands the understanding of intelligence beyond the conventional IQ framework. Gardner identifies eight distinct types of intelligence:
1.Linguistic Intelligence: The ability to use language effectively, whether in writing, speaking, or understanding spoken and written words.
2.Logical-Mathematical Intelligence: The capacity for logical reasoning, problem-solving, and mathematical calculations.
3.Spatial Intelligence: The skill to visualize and manipulate objects in a spatial context, crucial for architects, artists, and engineers.
4.Musical Intelligence: The talent for understanding, creating, and interpreting musical patterns and rhythms.
5.Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence: The ability to use one’s body skillfully for expressive or goal-directed purposes, seen in dancers, athletes, and surgeons.
6.Interpersonal Intelligence: The capacity to understand and interact effectively with others, a key trait for teachers, therapists, and leaders.
7.Intrapersonal Intelligence: The ability to understand oneself, including one’s emotions, motivations, and inner states.
8.Naturalistic Intelligence: The ability to recognize, categorize, and draw upon certain features of the environment, useful for biologists, farmers, and environmentalists.
Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence (EI) is another critical dimension of intelligence that has gained prominence. Coined by Daniel Goleman, EI refers to the ability to recognize, understand, manage, and utilize emotions effectively in oneself and others. It encompasses four key components:
Self-awareness:
Recognizing one’s emotions and their impact.
1.Self-regulation: Managing emotions in a healthy way.
2.Social awareness: Understanding the emotions of others.
3.Relationship management: Building and maintaining healthy relationships.
The Role of Genetics and Environment
Intelligence is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. While genetics provides the potential for certain cognitive abilities, environmental factors such as education, socio-economic status, nutrition, and cultural experiences play a significant role in shaping and enhancing that potential. The interaction between these factors determines the development and expression of intelligence in individuals.
Intelligence in the Modern World
In today’s rapidly changing world, the importance of intelligence goes beyond traditional academic success. The ability to adapt, learn continuously, and apply knowledge in various contexts is crucial. Technological advancements and globalization demand a broader range of skills, including creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence.
Moreover, the concept of collective intelligence, where diverse groups of people work together to solve problems and create knowledge, highlights the social dimension of intelligence. Collaborative efforts often lead to more innovative and effective solutions than individual endeavors.
Conclusion
Intelligence is a dynamic and multifaceted construct that cannot be fully captured by a single measure like IQ. Recognizing the diversity of cognitive abilities and the importance of emotional and social skills provides a more comprehensive understanding of human intelligence. As we navigate the complexities of the modern world, fostering a broad range of intelligences will be essential for personal growth and societal progress.Understanding Intelligence: Beyond IQ






